中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (3): 340-346.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.03.003
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
骨组织工程诱导性支架材料修复骨缺损
唐俊杰1,2,李文杰2,李 根2,王九娜2,赵 玲2,秦 文2,赵红斌1,2
- 1甘肃农业大学生命科学技术学院,甘肃省兰州市 730070;2解放军兰州军区兰州总医院,甘肃省兰州市 730050
Bone tissue engineering induced composite scaffolds for repair of bone defects
Tang Jun-jie1, 2, Li Wen-jie2, Li Gen2, Wang Jiu-na2, Zhao Ling2, Qin Wen2, Zhao Hong-bin1, 2
- 1College of Life Science and Technology, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou 730070, Gansu Province, China; 2Lanzhou General Hospital of Lanzhou Military Command, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China
摘要:
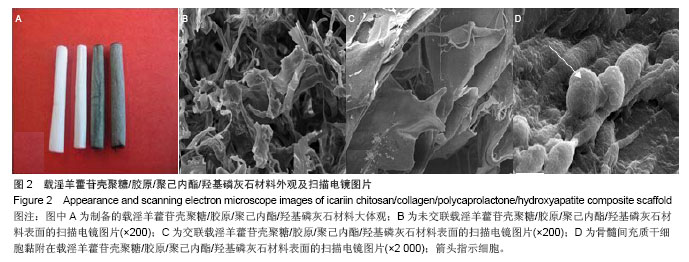
背景:前期实验中发现载淫羊藿苷壳聚糖/胶原/聚己内酯/羟基磷灰石复合支架具有良好的物理和化学性质。
目的:研究载淫羊藿苷壳聚糖/胶原/聚己内酯/羟基磷灰石复合支架修复兔胫骨平台骨缺损的效果。
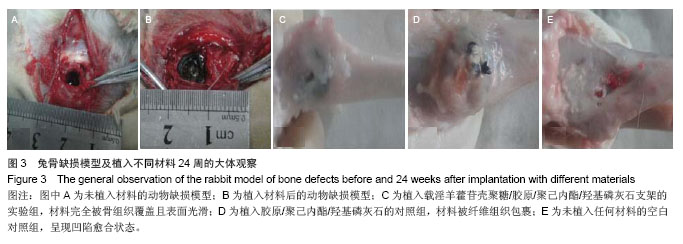
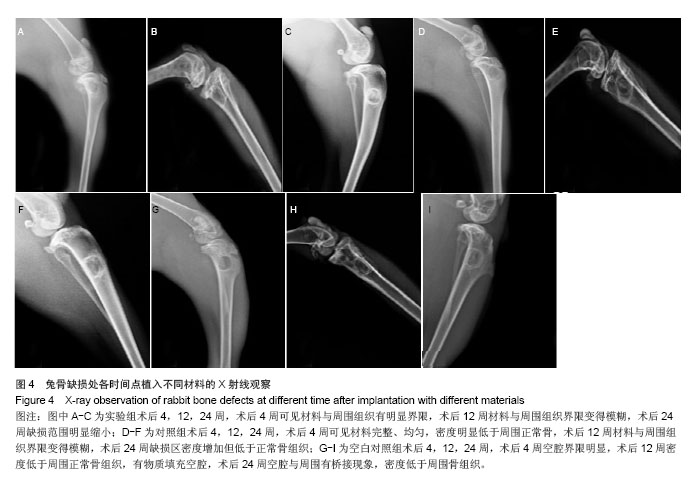
方法:利用静电纺丝技术制备胶原/聚己内酯/羟基磷灰石复合支架壳层,真空干燥法制备载淫羊藿苷壳聚糖微球/胶原支架芯层,将芯层嵌入壳层后利用京尼平交联构建载药复合支架。将载淫羊藿苷壳聚糖微球置入PBS中,观察药物缓释效果。将载药复合支架与大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞共培养7 d,观察细胞黏附效果。取青紫蓝兔15只,复制兔左侧胫骨缺损模型,随机分为3组,实验组于骨缺损处植入载药复合支架,对照组植入胶原/聚己内酯/羟基磷灰石复合支架,空白对照组不植入任何材料。术后4,12,24周行X射线观察、样本大体和组织学观察。
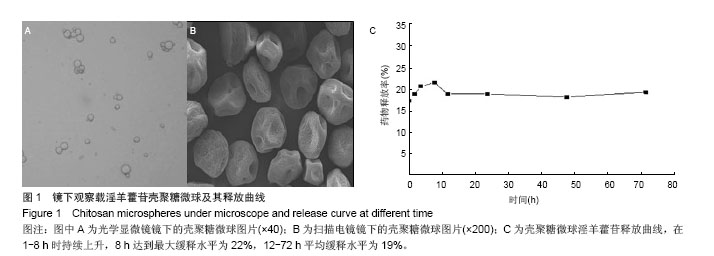
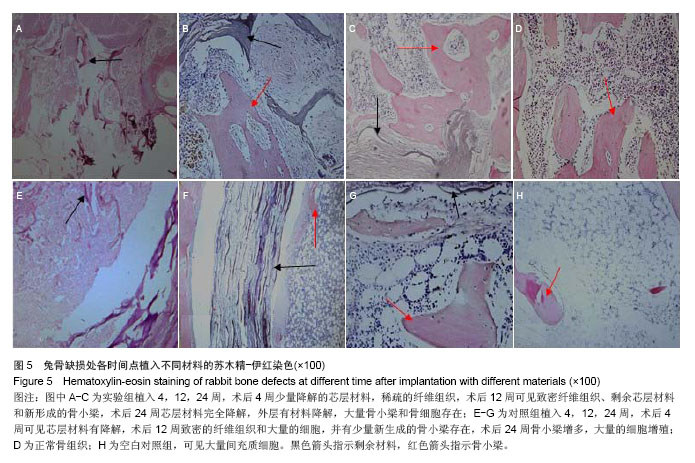
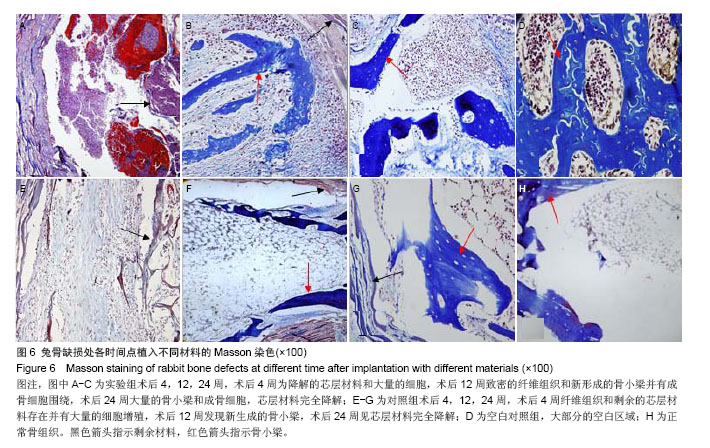
结果与结论:载药复合支架具有疏松多孔结构,利于骨髓间充质干细胞的黏附、增殖;壳聚糖微球体外缓释在72 h内保持19%释放量的良好缓释效果。术后24周,实验组材料完全被新生骨组织覆盖,硬度与正常骨相近,苏木精-伊红染色观察发现有骨小梁、骨细胞和成骨细胞,但缺损区骨密度低于正常骨组织;对照组材料被纤维组织包裹,苏木精-伊红染色显示有骨小梁、骨髓细胞和纤维组织;空白对照组呈凹陷愈合,但硬度低于正常骨组织,苏木精-伊红染色可见大量骨髓细胞和骨小梁。结果表明载药壳聚糖/胶原/聚己内酯/羟基磷灰石复合支架能有效修复兔骨缺损。
中图分类号:
.jpg)